NeuroTDPi:A Web-server for Prediction of neuro toxic compounds Using Depp Neural Network Model
Abstract
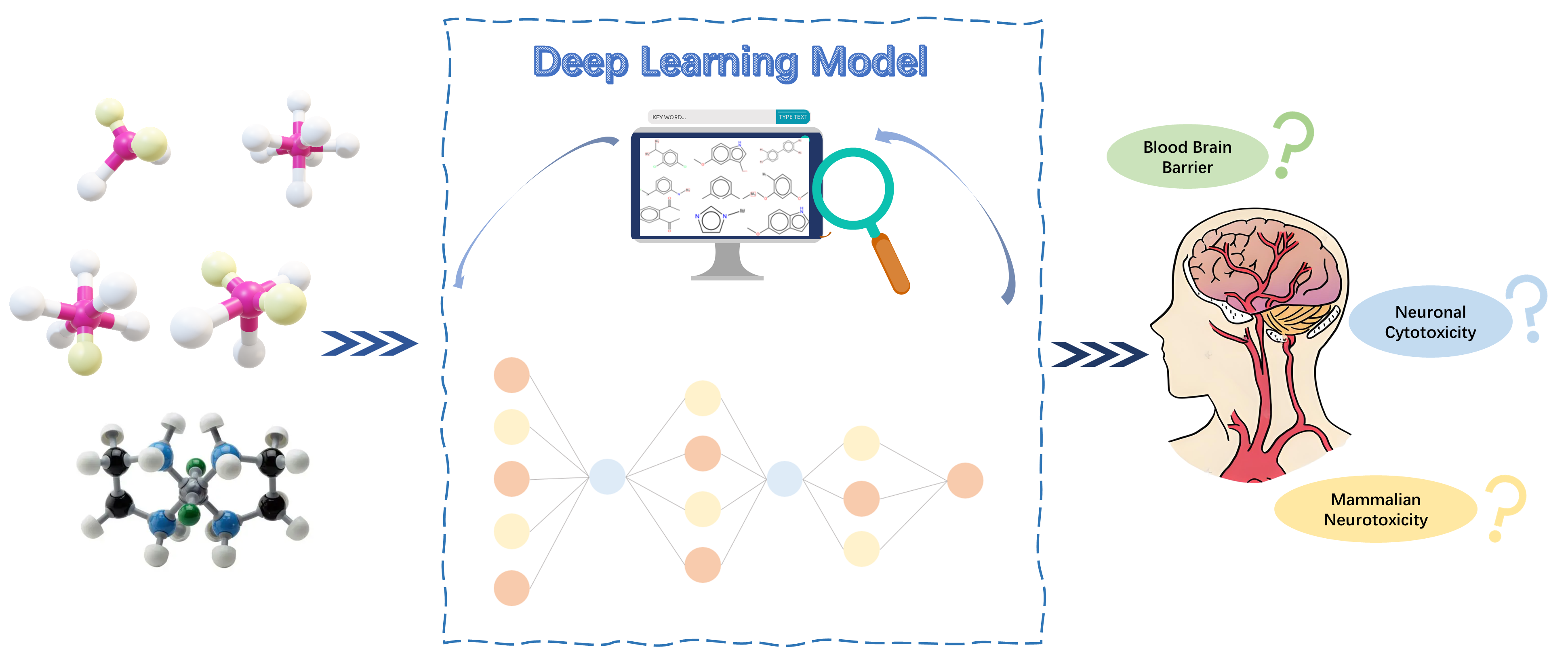
The mechanisms of neurotoxicity in natural products or synthetic compounds are complex and exhibit developmental stage specificity. Effective and reliable early toxicity prediction can reduce experimental costs. In this study, we employed a multi-modal fusion molecular representation to finely target three neurotoxicity endpoints: blood-brain barrier permeability, neuronal cytotoxicity, and mammalian neurotoxicity. We developed a multi-layer fully connected deep neural network model, NeuroTDPi. Further application of the Shapely method enhances model interpretability and characterizes the physicochemical properties of toxic compounds. The NeuroTDPi system demonstrated good ACU values for the three neurotoxicity endpoints, achieving 0.97, 0.84, and 0.82, respectively. Additionally, we mined and visualized alerting structures that may cause neurotoxicity, which could be responsible for potential neurotoxic effects. Our research can serve as a powerful tool for assessing neurotoxicity, and the SA system can intuitively provide molecular structural information for the neurotoxicity of compounds.
| Metrics | BBB | NT | NC |
| AUC | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.82 |
| ACC | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.77 |
| SE | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| SP | 0.93 | 0.81 | 0.67 |
| F1-Score | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.82 |